alanhope
Home, Music, Photography, Hifi, Web Design, Coding, Simulator, Chess, Synthesizers, Anaesthesia
Zebra 2
A complex, semi-modular synthesizer VSTI from U-he (Urs Heckman).
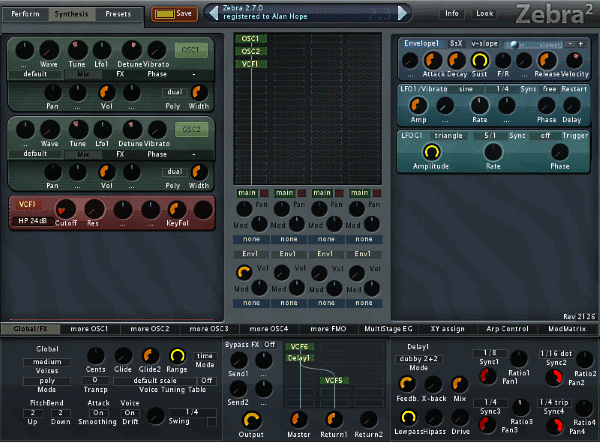
Looks pretty - what can you do with it? Here's a brief tutorial covering the absolute basics.
The Sound path
The sound generator is called an oscillator and Zebra has some fairly sophisticated ones. Each of these is set to produce a waveform and the traditional options are sine, saw, triangle, square / pwm (pulse-width-modulation). These all sound different: sine = flute-like, square = hollow, saw = buzzy, pwm = hollow with overtones.
In Zebra you can start with one or more oscillators, and can tune and fine-tune each of these.
Changing the tone
Various options here, let's look first at subtractive synthesis using a filter. Filters remove frequencies from the sound. Removing high frequencies (low-pass) makes it more muffled and bassy. Removing low frequencies (high-pass) more thin and trebly. Low-pass filter sweeps are a familiar synthesizer sound.
Movement
A sound can be static, or change slowly over time either once or repeatedly - this provides movement and interest to a sound. A low-frequency oscillator can act as a source of modulation of some part of the sound.